Chromatography is a process for separating components of a mixture and is widely applied in fields of fine chemistry, analytical chemistry, Organic Chemistry, Biochemistry, food safety, biomedicine, plant extraction, scientific analysis, environmental monitoring, petrochemicals, and many other fields.
How does Chromatography work?
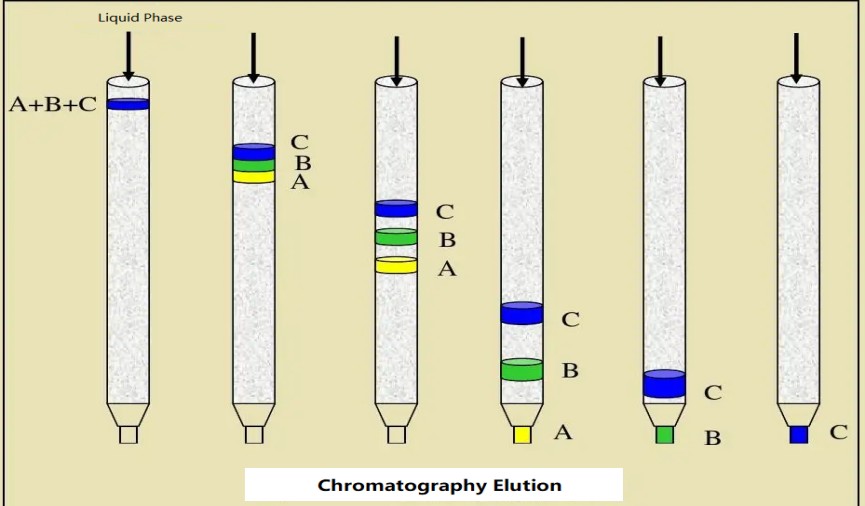
To start the process, we first dissolve the mixture in a substance called the mobile phase, and then the mixture is carried through a second substance called the stationary phase.
Based on the nature of the specific mobile and stationary phases, the different components of the mixture travel through the stationary phase at different speeds and eventually get separated from one another. It is the nature of the specific mobile and stationary phases that determines which substances travel more quickly or slowly, and that is how they are separated. These different travel times are called retention time. A wide variety of chromatographic methods have been developed by applying different mobile phases and stationary phases together with other factors determining traveling speed. Each method serves a different purpose and is ideal for different mixtures.
Applicaiton of Chromatography
There is preparative or analytical Chromatography. Preparative chromatography is a form of purification because it is used to separate the components of a mixture for later use. This process often comes with higher costs because it is set for scale production and requires a large number of materials. Analytical chromatography is normally done on a much smaller scale and uses smaller amounts of material. Its’ purpose is to establish the presence of different components or to measure the relative proportions of analytes in a mixture. These two different types of Chromatography often complement each other in practice and are not mutually exclusive.
People have developed many methods to use chromatography to separate compounds and the choice of methods lies in the physicochemical characteristics of the molecule to be separated. The stationary phases used for chromatography, also called chromatography media, are porous inert supports and can be functionalized with various chemical groups to dictate the interactions with the molecules to be separated.
In application, sensible choice of the right stationery phase or packing material is the core of Chromatography, for it plays a significant role in the results and efficiency of the extraction and purification process. Qingdao Bangkai Hi-tech Materials Co., Ltd is specialized in the research and manufacturing of chromatography-related materials and equipment with an individual R&D center. Based on their research and production practice, Silica gel is one of the most versatile and effective packing materials in chromatography and is also one of the most popular and widely used in fields like modern biomedicine, life science, fine chemistry, analytical chemistry, organic chemistry, biochemistry, food safety, plant extraction, scientific analysis, environment monitoring, petrochemicals, etc.,
Silica gel is a polar absorbent with slight acidity. It absorbs components in a mixture and can meanwhile remain neutral and maintain its own structure throughout the whole process. Silica-based packing material also features high mechanical strength and can endure high pressure and speed. Silica-based packing material produced by Qingdao Bangkai is newly developed by its R&D center and is with higher purity and lower metal content, higher reproducibility, and load capacity. One of Bangkai’s newly developed silica-based packing materials has been successfully validated to be used in electro-optical products. It can be customized upon request and is the ideal choice for the improvement of the separation&purification process and replacement of similar products in the international market.
Reference: WIKIPEDIA
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chromatography



